Search Physicians By:
ULTRASOUND
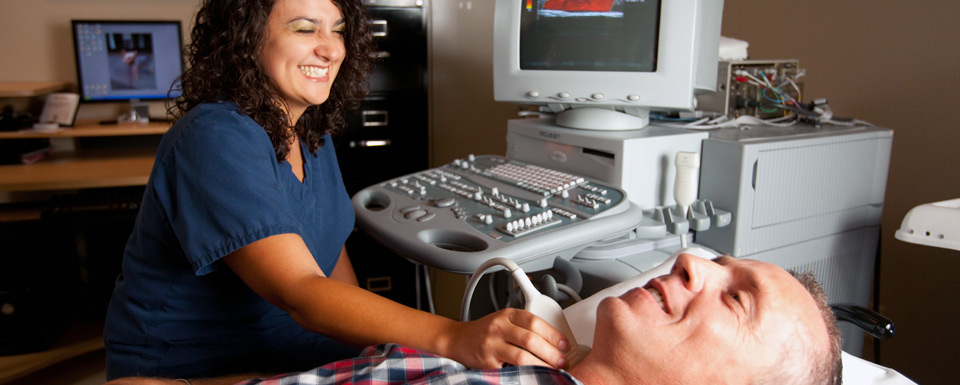
Ultrasound images help in the diagnosis of a wide range of diseases and conditions. During an ultrasound test, high-frequency sound waves, inaudible to the human ear, are transmitted through body tissues using an instrument called a transducer. The transducer transmits information to a computer that displays the image on a monitor.
Ultrasound is used to create images of soft tissue structures, such as the gallbladder, liver, heart, kidneys, pancreas, bladder, thyroid gland, prostate, female reproductive organs, and even of babies in the uterus. Ultrasound can also measure the flow of blood in the arteries to detect blockages.
How Can We Help You?
Find Us
COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SOUTH CAMPUS
3100 S.W. 89th Street
Oklahoma City, OK 73159
Directions
405.602.8100
COMMUNITY HOSPITAL NORTH IMAGING
9800 Broadway Extension
Oklahoma City, OK 73114
Directions
405.419.2980
OUTPATIENT THERAPY QUAIL POINTE
14024 Quail Pointe Drive
Oklahoma City, OK 73134
Directions
Website
405.340.2025
COMMUNITY HOSPITAL NORTH CAMPUS
9800 Broadway Extension
Oklahoma City, OK 73114
Directions
405.419.2980
COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SOUTH IMAGING
3100 S.W. 89th Street
Oklahoma City, OK 73159
Directions
405.602.8100
OUTPATIENT THERAPY SOUTH
10001 S. Western Ave., Ste 102
Oklahoma City, OK 73139
Directions
Website
405.691.5434
NORTHWEST SURGICAL
HOSPITAL
9204 North May Avenue
Oklahoma City, OK 73120
Directions
Website
405.848.1918
OUTPATIENT HAND THERAPY SOUTH
10001 S. Western Ave., Ste 204
Oklahoma City, OK 73139
Directions
Website
405.427.3752